Traefik
作者: ryan 发布于: 8/17/2025 更新于: 8/17/2025 字数: 0 字 阅读: 0 分钟
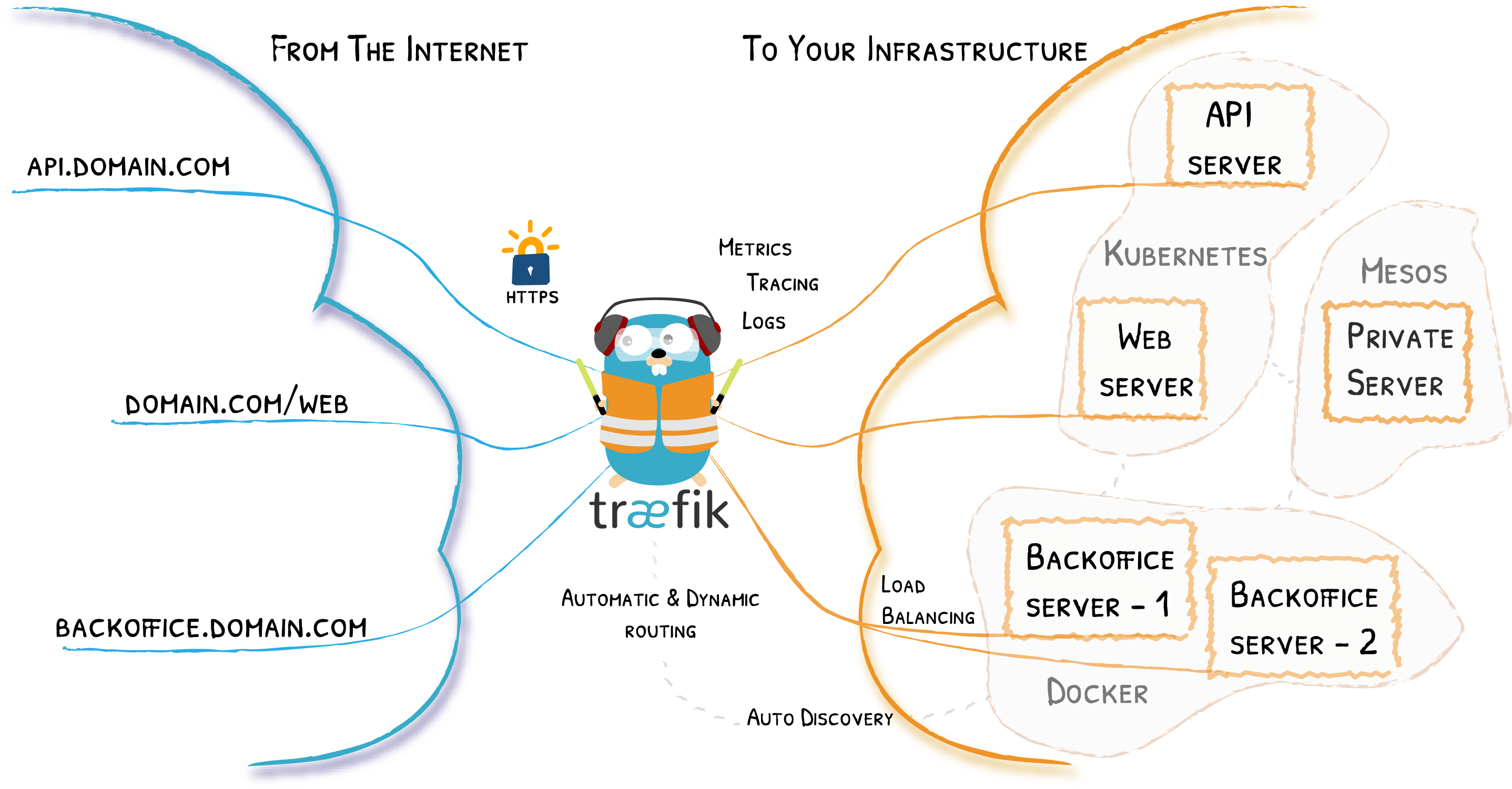
Traefik 是一个开源的可以使服务发布变得轻松有趣的边缘路由器。它负责接收你系统的请求,然后使用合适的组件来对这些请求进行处理。
除了众多的功能之外,Traefik 的与众不同之处还在于它会自动发现适合你服务的配置。当 Traefik 在检查你的服务时,会找到服务的相关信息并找到合适的服务来满足对应的请求。
Traefik 兼容所有主流的集群技术,比如 Kubernetes,Docker,Docker Swarm,AWS,Mesos,Marathon,等等;并且可以同时处理多种方式。(甚至可以用于在裸机上运行的比较旧的软件。)
使用 Traefik,不需要维护或者同步一个独立的配置文件:因为一切都会自动配置,实时操作的(无需重新启动,不会中断连接)。
使用 Traefik,你可以花更多的时间在系统的开发和新功能上面,而不是在配置和维护工作状态上面花费大量时间。
核心概念
Traefik 是一个边缘路由器,是你整个平台的大门,拦截并路由每个传入的请求:它知道所有的逻辑和规则,这些规则确定哪些服务处理哪些请求;
传统的反向代理需要一个配置文件,其中包含路由到你服务的所有可能路由,而 Traefik 会实时检测服务并自动更新路由规则,可以自动服务发现。
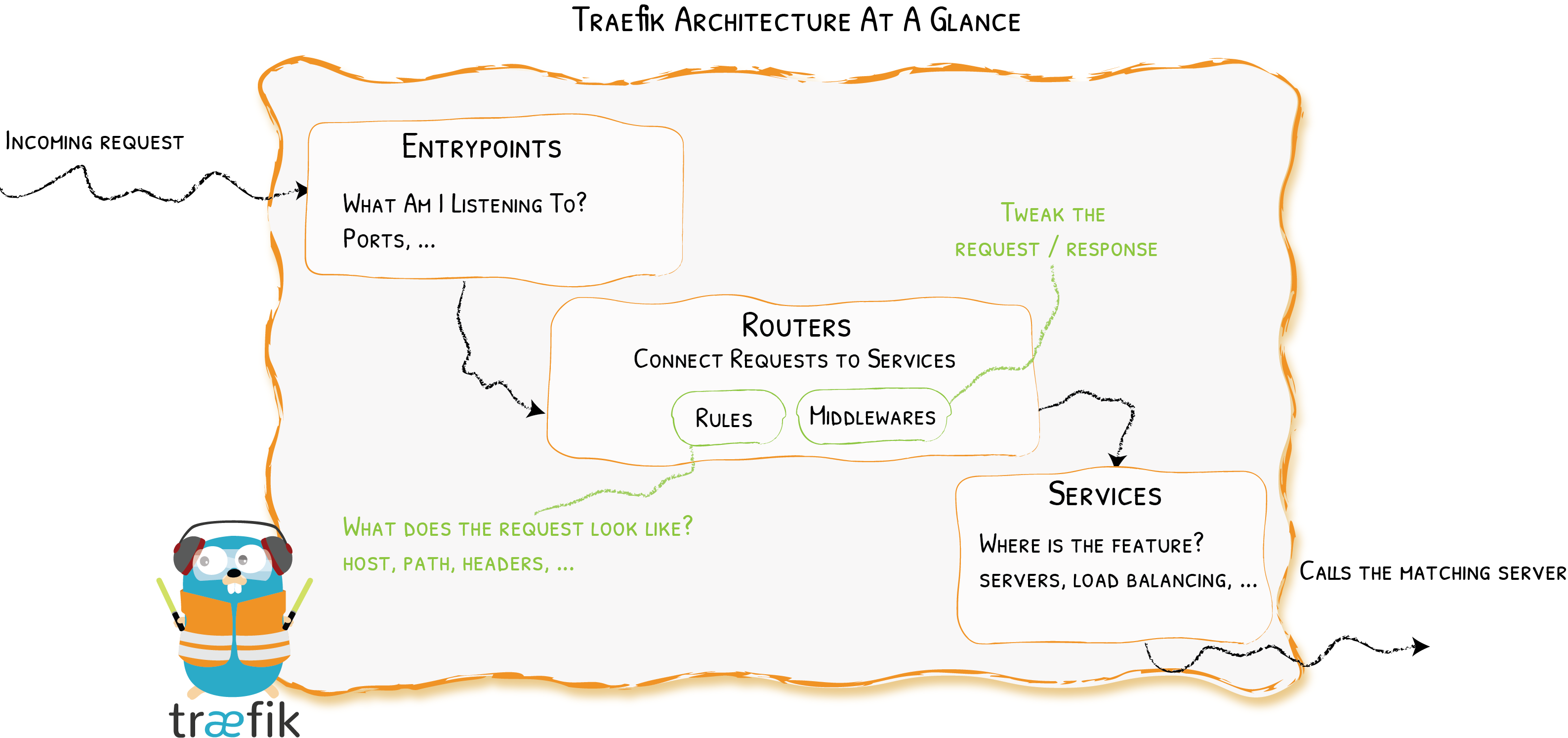
首先,当启动 Traefik 时,需要定义 entrypoints(入口点),然后,根据连接到这些 entrypoints 的路由来分析传入的请求,来查看他们是否与一组规则相匹配,如果匹配,则路由可能会将请求通过一系列中间件转换过后再转发到你的服务上去。
在了解 Traefik 之前有几个核心概念我们必须要了解:
- Providers 用来自动发现平台上的服务,可以是编排工具、容器引擎或者 key-value 存储等,比如 Docker、Kubernetes、File
- Entrypoints 监听传入的流量(端口等…),是网络入口点,它们定义了接收请求的端口(HTTP 或者 TCP)。
- Routers 分析请求(host, path, headers, SSL, …),负责将传入请求连接到可以处理这些请求的服务上去。
- Services 将请求转发给你的应用(load balancing, …),负责配置如何获取最终将处理传入请求的实际服务。
- Middlewares 中间件,用来修改请求或者根据请求来做出一些判断(authentication, rate limiting, headers, ...),中间件被附件到路由上,是一种在请求发送到你的服务之前(或者在服务的响应发送到客户端之前)调整请求的一种方法。
Traefik 流量全生命周期
在 Kubernetes 集群中,Traefik 作为 Ingress 控制器负责将外部的流量路由到内部的服务。理解 Traefik 的流量全生命周期,可以帮助我们清楚地了解从流量进入集群到最终被服务处理的整个过程。
外部请求
↓
外部负载均衡/节点公开端口
↓
Traefik (TLS 终止,Ingress 路由)
↓
负载均衡 (轮询、权重等)
↓
Kubernetes 服务
↓
后端 Pod (服务处理)
↓
服务响应
↓
Traefik 中间件处理 (日志、压缩等)
↓
返回给外部客户端流量入口
外部用户的请求首先通过外部访问点(如浏览器或 API 客户端)发起,这个请求会通过集群的外部负载均衡器或直接到达集群节点的公开端口。
通常会有一个外部的负载均衡器负责将请求分发到多个 Kubernetes 节点。流量会直接进入暴露了 Traefik 的节点端口。
接收请求
流量进入集群后,首先由 Traefik 作为 Ingress 控制器接收请求。
Traefik 通常监听指定的端口(如 80 和 443)来处理 HTTP 和 HTTPS 流量。如果是 HTTPS 请求,Traefik 会处理 TLS 终止,包括解密 SSL/TLS 流量。
路由规则解析
Traefik 根据预先配置的路由规则(来自 Kubernetes 的 Ingress 资源或 Traefik 的配置文件)来决定如何将请求转发到集群内部的具体服务。
Traefik 支持中间件机制,在路由请求之前,可以对请求应用一系列的中间件功能(如认证、限速、重定向、缓存等)。
负载均衡
根据路由规则,Traefik 将请求分发到目标服务。Traefik 提供多种负载均衡策略,例如:
- 轮询 (Round Robin): 默认情况下,Traefik 会将流量按轮询的方式分配给服务的不同实例。
- 随机 (Random): 另一种负载均衡策略是随机选择服务实例。
- 权重 (Weighted): Traefik 可以根据权重配置,分配更多流量到某些特定的服务实例。
服务处理请求
请求被 Traefik 路由并负载均衡后,进入具体的后端服务处理。服务可以是任何 Kubernetes 中运行的 Pod,它通过服务抽象(Service)进行暴露。
响应返回
后端服务生成响应并将其通过 Kubernetes 服务返回给 Traefik,Traefik 随后会将响应发送回请求的源(即外部客户端)。
Traefik 在返回响应时,可能会应用一些中间件功能,比如在返回响应前进行压缩、修改头部等操作。
Traefik 可以记录详细的请求和响应日志,用于后续的监控和调试。
监控和日志
整个过程中,Traefik 提供了强大的监控和日志功能:
Traefik 内置了 Dashboard,可以实时监控流量的路由、健康检查、服务状态等。可以输出详细的日志,包括请求路径、响应时间、状态码等信息。
Traefik 支持与 Prometheus 等监控系统集成,提供丰富的指标供监控和告警使用。
动态配置管理
raefik 具备动态配置功能,能够自动检测服务和路由变化,当 Kubernetes 集群中的服务发生变化时,Traefik 会自动更新路由规则,无需手动重启或修改配置。
Traefik 可以在不中断现有流量的情况下,动态更新配置并应用新的路由规则。
Traefik 和 ingress-nginx 有什么区别?
架构设计
Traefik 是一个云原生的反向代理和负载均衡器,专门为动态基础设施设计(如容器化环境)。它可以通过多个提供者(如 Kubernetes、Docker、Rancher)标签或注解自动发现服务,并能根据流量动态调整,而无需手动重启服务。
Ingress-NGINX 基于 NGINX,是 Kubernetes 社区维护的最常用的 Ingress 控制器之一。它专注于 Kubernetes Ingress 资源的管理和路由,主要针对 HTTP 和 HTTPS 流量,虽然也可以通过自定义配置支持 TCP/UDP,但这并不是它的核心功能。
Ingress-NGINX 不具备动态路由检测的功能,每次配置更改后,NGINX 通常需要重新加载配置。
配置和管理
Traefik 不仅支持 HTTP 和 HTTPS,还支持 TCP 和 UDP 路由,这使得它更灵活,适用于更多种类的应用程序。而且Traefik 还有一个内置的仪表盘,可以通过 Dashboard 或 REST API 动态更新路由配置实时查看和监控路由配置和流量情况。
配置基于 Kubernetes Ingress 资源和 NGINX 特有的注解,功能强大且成熟,但配置管理相对传统,需要在 Ingress 资源中手动指定规则。
Ingress-NGINX 依赖 NGINX 本身的配置文件模式,并通过注解提供自定义 NGINX 配置。
性能
Traefik 使用 Go 语言开发,性能高效在处理 HTTP/HTTPS 流量时,Traefik 的性能与 Ingress-NGINX 相近,但在处理大量动态服务或频繁配置变更时,Traefik 具有一定优势。
Ingress-NGINX 基于 NGINX,NGINX 本身是成熟的 Web 服务器和反向代理,因此性能非常好,特别是在处理静态内容或高并发 HTTP 请求时。在非常复杂的场景下,如需要大量细粒度的配置,Ingress-NGINX 可能更加高效,尤其是在静态配置场景。
功能扩展性
Traefik 支持多种认证方式、负载均衡策略、限速、重定向等功能,还原生支持 ACME(Let’s Encrypt)自动管理证书,适合 HTTPS 的动态管理。
Traefik 内置对 gRPC 的支持,并可以通过中间件扩展功能(如身份验证、重试机制、限流等)。
Ingress-NGINX 基于 NGINX 的功能,因此它能使用 NGINX 的完整功能集,特别是对于复杂的 HTTP 配置,支持范围广泛,如高级缓存、复杂的反向代理规则等。通过 NGINX 的扩展模块,Ingress-NGINX 可以提供很多高级功能,如基于 IP 的访问控制、限速、缓存等。
社区生态
Traefik 的用户和社区增长较快,它的云原生架构受到 DevOps 和容器用户的青睐。
Traefik 的文档和支持丰富,特别是在 Docker 和 Kubernetes 社区中,Traefik 作为负载均衡器和 Ingress 控制器的普及率很高。
Ingress-NGINX 是 Kubernetes 社区的官方项目之一,使用广泛,文档全面,适合需要 NGINX 特性和社区支持的场景。
社区维护的稳定性和长期支持使得 Ingress-NGINX 成为许多企业的首选。
安装Traefik
由于 Traefik 2.X 版本和之前的 1.X 版本不兼容,我们这里选择功能更加强大的 2.X 版本来和大家进行讲解。
在 Traefik 中的配置可以使用两种不同的方式:
- 动态配置:管理与路由相关的设置,随着环境的变化(如服务的启动、终止、扩展等)而自动更新。
- 静态配置:Traefik 在启动时加载的配置
静态配置中的元素(这些元素不会经常更改,这些配置在 Traefik 启动后不会自动更改,除非重新启动 Traefik 实例)连接到 providers 并定义 Treafik 将要监听的 entrypoints。
在 Traefik 中有三种方式定义静态配置:在配置文件中、在命令行参数中、通过环境变量传递
动态配置包含定义系统如何处理请求的所有配置内容,这些配置是可以改变的,而且是无缝热更新的,没有任何请求中断或连接损耗。
版本支持
Kubernetes 版本支持
由于 CRD 版本支持的变化,下列版本的 Chart 可以在以下 Kubernetes 版本中使用和支持:
| Kubernetes 版本 | Kubernetes v1.15 及以下 | Kubernetes v1.16 - v1.21 | Kubernetes v1.22 及以上 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chart v9.20.2 及以下 | [✔] | [✔] | |
| Chart v10.0.0 及以上 | [✔] | [✔] | |
| Chart v22.0.0 及以上 | [✔] |
- Kubernetes v1.15 及以下 支持 Chart v9.20.2 及以下版本。
- Kubernetes v1.16 - v1.21 支持 Chart v9.20.2 及以下版本,以及 v10.0.0 及以上版本。
- Kubernetes v1.22 及以上 仅支持 Chart v10.0.0 及以上版本,其中 Chart v22.0.0 及以上版本专门为 v1.22 及以上的 Kubernetes 提供支持。
详细信息:https://github.com/traefik/traefik-helm-chart?tab=readme-ov-file#kubernetes-version-support
helm 安装traefik
这里我们还是使用 Helm 来快速安装 traefik,我们的 K8S 集群是 1.22.2 版本,我们选择v23.2.0版本
首先获取 Helm Chart 包:
https://github.com/traefik/traefik-helm-chart/releases/tag/v23.2.0
$ git clone --branch v23.2.0 https://github.com/traefik/traefik-helm-chart.git
$ cd traefik-helm-chart定制values配置
仅 Host 主机模式
创建一个定制的 values 配置文件:
# ci/deployment-prod.yaml
deployment:
enabled: true
kind: Deployment
# 使用 IngressClass. Traefik 版本<2.3 或者 Kubernetes 版本 < 1.18.x 会被忽略
ingressClass:
# 还没有进行完整的单元测试,pending https://github.com/rancher/helm-unittest/pull/12
enabled: true
isDefaultClass: false
ingressRoute: # 不用自动创建,我们自己处理
dashboard:
enabled: false
#
# 配置 providers
#
providers:
kubernetesCRD: # 开启 crd provider
enabled: true
allowCrossNamespace: true # 是否允许跨命名空间
allowExternalNameServices: true # 是否允许使用 ExternalName 的服务
kubernetesIngress: # 开启 ingress provider
enabled: true
allowExternalNameServices: true
logs:
general:
# format: json
level: DEBUG
access:
enabled: true
ports:
web:
port: 8000
hostPort: 80 # 使用 hostport 模式
websecure:
port: 8443
hostPort: 443 # 使用 hostport 模式
metrics:
port: 9100
hostPort: 9101
service: # host 模式就不需要创建 Service 了,云端环境可以用 Service 模式
enabled: false
resources:
requests:
cpu: '100m'
memory: '100Mi'
limits:
cpu: '100m'
memory: '100Mi'
# tolerations: # kubeadm 安装的集群默认情况下master是有污点,如果需要安装在master节点需要添加容忍
# - key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master"
# operator: "Equal"
# effect: "NoSchedule"
nodeSelector: # 固定到node1这个边缘节点
kubernetes.io/hostname: 'node1'这里我们使用 hostport 模式将 Traefik 固定到 node1 节点上,因为只有这个节点有外网 IP,所以我们这里 node1 是作为流量的入口点。直接使用上面的 values 文件安装 traefik:
NodePort 模式
# Default values for Traefik
image:
# -- Traefik image host registry
registry: registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com
# -- Traefik image repository
repository: xxk8s/traefik
# -- defaults to appVersion
tag: "v2.10.4"
# -- Traefik image pull policy
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# -- Add additional label to all resources
commonLabels: {}
#
# Configure the deployment
#
deployment:
# -- Enable deployment
enabled: true
# -- Deployment or DaemonSet
kind: Deployment
# -- Number of pods of the deployment (only applies when kind == Deployment)
replicas: 1
# -- Number of old history to retain to allow rollback (If not set, default Kubernetes value is set to 10)
# revisionHistoryLimit: 1
# -- Amount of time (in seconds) before Kubernetes will send the SIGKILL signal if Traefik does not shut down
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 60
# -- The minimum number of seconds Traefik needs to be up and running before the DaemonSet/Deployment controller considers it available
minReadySeconds: 0
# -- Additional deployment annotations (e.g. for jaeger-operator sidecar injection)
annotations: {}
# -- Additional deployment labels (e.g. for filtering deployment by custom labels)
labels: {}
# -- Additional pod annotations (e.g. for mesh injection or prometheus scraping)
podAnnotations: {}
# -- Additional Pod labels (e.g. for filtering Pod by custom labels)
podLabels: {}
# -- Additional containers (e.g. for metric offloading sidecars)
additionalContainers: []
# socat用于将 UDP 流量转发到 Unix 套接字
# socat容器的功能是在 UDP 和 Unix 套接字之间进行数据转发
# 这在 Traefik 默认配置中并不支持,因此必须借助该额外的辅助容器来实现这个功能。
# 监听 UDP 8125 端口,并将接收到的 UDP 数据通过 Unix 套接字/socket/socket转发
# https://docs.datadoghq.com/developers/dogstatsd/unix_socket/?tab=host
# - name: socat-proxy
# image: alpine/socat:1.0.5
# args: ["-s", "-u", "udp-recv:8125", "unix-sendto:/socket/socket"]
# volumeMounts:
# - name: dsdsocket
# mountPath: /socket
# -- Additional volumes available for use with initContainers and additionalContainers
additionalVolumes: []
# 用来声明额外卷的字段,可以在initContainers 或additionalContainers中使用这些卷
# - name: dsdsocket
# hostPath:
# path: /var/run/statsd-exporter
# -- Additional initContainers (e.g. for setting file permission as shown below)
initContainers: []
# 在主容器启动之前执行的初始化容器,通常用于初始化文件权限、预处理数据等任务。
# The "volume-permissions" init container is required if you run into permission issues.
# Related issue: https://github.com/traefik/traefik-helm-chart/issues/396
# - name: volume-permissions
# image: busybox:latest
# command: ["sh", "-c", "touch /data/acme.json; chmod -v 600 /data/acme.json"]
# securityContext:
# runAsNonRoot: true
# runAsGroup: 65532
# runAsUser: 65532
# volumeMounts:
# - name: data
# mountPath: /data
# -- Use process namespace sharing
# 配置Pod 中的容器是否共享同一个进程命名空间
shareProcessNamespace: false
# -- Custom pod DNS policy. Apply if `hostNetwork: true`
# dnsPolicy: ClusterFirstWithHostNet
dnsConfig: {}
# nameservers:
# - 192.0.2.1 # this is an example
# searches:
# - ns1.svc.cluster-domain.example
# - my.dns.search.suffix
# options:
# - name: ndots
# value: "2"
# - name: edns0
# -- Additional imagePullSecrets
imagePullSecrets: []
# - name: myRegistryKeySecretName
# -- Pod lifecycle actions
# lifecycle钩子允许在容器的生命周期中的特定时刻执行一些自定义操作
lifecycle: {}
# preStop:
# exec:
# command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "sleep 40"]
# postStart:
# httpGet:
# path: /ping
# port: 9000
# host: localhost
# scheme: HTTP
# -- Pod disruption budget
# 定义最大允许中断的 Pod 数量
podDisruptionBudget:
enabled: false
# maxUnavailable: 1
# maxUnavailable: 33%
# minAvailable: 0
# minAvailable: 25%
# -- Create a default IngressClass for Traefik
ingressClass:
enabled: true
isDefaultClass: false
name: traefik-class
# name: my-custom-class
# Traefik experimental features
# 实验特性
experimental:
#This value is no longer used, set the image.tag to a semver higher than 3.0, e.g. "v3.0.0-beta3"
#v3:
# -- Enable traefik version 3
# enabled: false
plugins:
# -- Enable traefik experimental plugins
enabled: false
kubernetesGateway:
# Kubernetes 中的一个新特性,用于取代和扩展现有的 Ingress API
# -- Enable traefik experimental GatewayClass CRD
enabled: false
gateway:
# -- Enable traefik regular kubernetes gateway
enabled: true
# certificate:
# group: "core"
# kind: "Secret"
# name: "mysecret"
# -- By default, Gateway would be created to the Namespace you are deploying Traefik to.
# You may create that Gateway in another namespace, setting its name below:
# namespace: default
# Additional gateway annotations (e.g. for cert-manager.io/issuer)
# annotations:
# cert-manager.io/issuer: letsencrypt
## Create an IngressRoute for the dashboard
## 定义一个Traefik Dashboard 的 IngressRoute 配置
ingressRoute:
dashboard:
# -- Create an IngressRoute for the dashboard
enabled: false
# -- Additional ingressRoute annotations (e.g. for kubernetes.io/ingress.class)
annotations: {}
# -- Additional ingressRoute labels (e.g. for filtering IngressRoute by custom labels)
labels: {}
# -- The router match rule used for the dashboard ingressRoute
matchRule: PathPrefix(`/dashboard`) || PathPrefix(`/api`)
# -- Specify the allowed entrypoints to use for the dashboard ingress route, (e.g. traefik, web, websecure).
# By default, it's using traefik entrypoint, which is not exposed.
# /!\ Do not expose your dashboard without any protection over the internet /!\
entryPoints: ["traefik"]
# -- Additional ingressRoute middlewares (e.g. for authentication)
middlewares: []
# -- TLS options (e.g. secret containing certificate)
tls: {}
updateStrategy:
# 升级策略滚动更新
# -- Customize updateStrategy: RollingUpdate or OnDelete
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 0
maxSurge: 1
readinessProbe:
# -- The number of consecutive failures allowed before considering the probe as failed.
failureThreshold: 1
# -- The number of seconds to wait before starting the first probe.
initialDelaySeconds: 2
# -- The number of seconds to wait between consecutive probes.
periodSeconds: 10
# -- The minimum consecutive successes required to consider the probe successful.
successThreshold: 1
# -- The number of seconds to wait for a probe response before considering it as failed.
timeoutSeconds: 2
livenessProbe:
# -- The number of consecutive failures allowed before considering the probe as failed.
failureThreshold: 3
# -- The number of seconds to wait before starting the first probe.
initialDelaySeconds: 2
# -- The number of seconds to wait between consecutive probes.
periodSeconds: 10
# -- The minimum consecutive successes required to consider the probe successful.
successThreshold: 1
# -- The number of seconds to wait for a probe response before considering it as failed.
timeoutSeconds: 2
providers:
kubernetesCRD:
#Kubernetes CRD 提供者的配置
# -- Load Kubernetes IngressRoute provider
enabled: true
# -- Allows IngressRoute to reference resources in namespace other than theirs
# 控制是否允许 IngressRoute 引用来自其他命名空间的资源
allowCrossNamespace: true
# -- Allows to reference ExternalName services in IngressRoute
# 控制是否允许 IngressRoute 引用 Kubernetes 中的 ExternalName 服务
allowExternalNameServices: true
# 控制是否允许当服务没有可用的 endpoints 时,Traefik 返回 503 错误
# -- Allows to return 503 when there is no endpoints available
allowEmptyServices: true
# ingressClass: traefik-internal
# labelSelector: environment=production,method=traefik
# -- Array of namespaces to watch. If left empty, Traefik watches all namespaces.
namespaces: []
# - "default"
kubernetesIngress:
# 设置为 true 时,Traefik 将能够管理和处理集群中的 Kubernetes Ingress 资源
# -- Load Kubernetes IngressRoute provider
enabled: true
# -- Allows to reference ExternalName services in Ingress
allowExternalNameServices: true
# -- Allows to return 503 when there is no endpoints available
allowEmptyServices: true
# ingressClass: traefik-internal
# labelSelector: environment=production,method=traefik
# -- Array of namespaces to watch. If left empty, Traefik watches all namespaces.
namespaces: []
# - "default"
# IP used for Kubernetes Ingress endpoints
publishedService:
enabled: false
# publishedService 控制 Traefik 如何获取和使用其对外暴露的 IP 地址信息。
# 通常在基于云环境的 LoadBalancer 服务中使用,以确保负载均衡器的 IP 被正确发布到 Kubernetes 中
# Published Kubernetes Service to copy status from. Format: namespace/servicename
# By default this Traefik service
# pathOverride: ""
#
# -- Add volumes to the traefik pod. The volume name will be passed to tpl.
# This can be used to mount a cert pair or a configmap that holds a config.toml file.
# After the volume has been mounted, add the configs into traefik by using the `additionalArguments` list below, eg:
# `additionalArguments:
# - "--providers.file.filename=/config/dynamic.toml"
# - "--ping"
# - "--ping.entrypoint=web"`
volumes: []
# - name: public-cert
# mountPath: "/certs"
# type: secret
# - name: '{{ printf "%s-configs" .Release.Name }}'
# mountPath: "/config"
# type: configMap
# -- Additional volumeMounts to add to the Traefik container
additionalVolumeMounts: []
# -- For instance when using a logshipper for access logs
# - name: traefik-logs
# mountPath: /var/log/traefik
logs:
general:
# -- By default, the logs use a text format (common), but you can
# also ask for the json format in the format option
# format: json
# By default, the level is set to ERROR.
# -- Alternative logging levels are DEBUG, PANIC, FATAL, ERROR, WARN, and INFO.
level: ERROR
access:
# -- To enable access logs
enabled: false
## By default, logs are written using the Common Log Format (CLF) on stdout.
## To write logs in JSON, use json in the format option.
## If the given format is unsupported, the default (CLF) is used instead.
# format: json
# filePath: "/var/log/traefik/access.log
## To write the logs in an asynchronous fashion, specify a bufferingSize option.
## This option represents the number of log lines Traefik will keep in memory before writing
## them to the selected output. In some cases, this option can greatly help performances.
# bufferingSize: 100
## Filtering
# -- https://docs.traefik.io/observability/access-logs/#filtering
filters: {}
# statuscodes: "200,300-302"
# retryattempts: true
# minduration: 10ms
fields:
general:
# -- Available modes: keep, drop, redact.
defaultmode: keep
# -- Names of the fields to limit.
names: {}
## Examples:
# ClientUsername: drop
headers:
# -- Available modes: keep, drop, redact.
defaultmode: drop
# -- Names of the headers to limit.
names: {}
## Examples:
# User-Agent: redact
# Authorization: drop
# Content-Type: keep
metrics:
## 配置Prometheus 监控 Traefik 的各种性能指标
## -- Prometheus is enabled by default.
## -- It can be disabled by setting "prometheus: null"
## 如果设置为 null,可以禁用 Prometheus 的 metrics 监控功能。
prometheus:
# -- Entry point used to expose metrics.
entryPoint: metrics
## 定义用于暴露 Prometheus metrics 的入口点
## Enable metrics on entry points. Default=true
## 启用或禁用在入口点上添加标签
# addEntryPointsLabels: false
## 启用或禁用在路由上添加标签
## Enable metrics on routers. Default=false
# addRoutersLabels: true
## 启用或禁用在服务上添加标签
## Enable metrics on services. Default=true
# addServicesLabels: false
## Buckets for latency metrics. Default="0.1,0.3,1.2,5.0"
## 设置用于计算延迟分布的桶buckets
# buckets: "0.5,1.0,2.5"
## When manualRouting is true, it disables the default internal router in
## order to allow creating a custom router for prometheus@internal service.
## 禁用默认的内部路由器,允许手动配置 Prometheus 路由。
# manualRouting: true
# datadog:
# ## Address instructs exporter to send metrics to datadog-agent at this address.
# address: "127.0.0.1:8125"
# ## The interval used by the exporter to push metrics to datadog-agent. Default=10s
# # pushInterval: 30s
# ## The prefix to use for metrics collection. Default="traefik"
# # prefix: traefik
# ## Enable metrics on entry points. Default=true
# # addEntryPointsLabels: false
# ## Enable metrics on routers. Default=false
# # addRoutersLabels: true
# ## Enable metrics on services. Default=true
# # addServicesLabels: false
# influxdb:
# ## Address instructs exporter to send metrics to influxdb at this address.
# address: localhost:8089
# ## InfluxDB's address protocol (udp or http). Default="udp"
# protocol: udp
# ## InfluxDB database used when protocol is http. Default=""
# # database: ""
# ## InfluxDB retention policy used when protocol is http. Default=""
# # retentionPolicy: ""
# ## InfluxDB username (only with http). Default=""
# # username: ""
# ## InfluxDB password (only with http). Default=""
# # password: ""
# ## The interval used by the exporter to push metrics to influxdb. Default=10s
# # pushInterval: 30s
# ## Additional labels (influxdb tags) on all metrics.
# # additionalLabels:
# # env: production
# # foo: bar
# ## Enable metrics on entry points. Default=true
# # addEntryPointsLabels: false
# ## Enable metrics on routers. Default=false
# # addRoutersLabels: true
# ## Enable metrics on services. Default=true
# # addServicesLabels: false
# influxdb2:
# ## Address instructs exporter to send metrics to influxdb v2 at this address.
# address: localhost:8086
# ## Token with which to connect to InfluxDB v2.
# token: xxx
# ## Organisation where metrics will be stored.
# org: ""
# ## Bucket where metrics will be stored.
# bucket: ""
# ## The interval used by the exporter to push metrics to influxdb. Default=10s
# # pushInterval: 30s
# ## Additional labels (influxdb tags) on all metrics.
# # additionalLabels:
# # env: production
# # foo: bar
# ## Enable metrics on entry points. Default=true
# # addEntryPointsLabels: false
# ## Enable metrics on routers. Default=false
# # addRoutersLabels: true
# ## Enable metrics on services. Default=true
# # addServicesLabels: false
# statsd:
# ## Address instructs exporter to send metrics to statsd at this address.
# address: localhost:8125
# ## The interval used by the exporter to push metrics to influxdb. Default=10s
# # pushInterval: 30s
# ## The prefix to use for metrics collection. Default="traefik"
# # prefix: traefik
# ## Enable metrics on entry points. Default=true
# # addEntryPointsLabels: false
# ## Enable metrics on routers. Default=false
# # addRoutersLabels: true
# ## Enable metrics on services. Default=true
# # addServicesLabels: false
# openTelemetry:
# ## Address of the OpenTelemetry Collector to send metrics to.
# address: "localhost:4318"
# ## Enable metrics on entry points.
# addEntryPointsLabels: true
# ## Enable metrics on routers.
# addRoutersLabels: true
# ## Enable metrics on services.
# addServicesLabels: true
# ## Explicit boundaries for Histogram data points.
# explicitBoundaries:
# - "0.1"
# - "0.3"
# - "1.2"
# - "5.0"
# ## Additional headers sent with metrics by the reporter to the OpenTelemetry Collector.
# headers:
# foo: bar
# test: test
# ## Allows reporter to send metrics to the OpenTelemetry Collector without using a secured protocol.
# insecure: true
# ## Interval at which metrics are sent to the OpenTelemetry Collector.
# pushInterval: 10s
# ## Allows to override the default URL path used for sending metrics. This option has no effect when using gRPC transport.
# path: /foo/v1/traces
# ## Defines the TLS configuration used by the reporter to send metrics to the OpenTelemetry Collector.
# tls:
# ## The path to the certificate authority, it defaults to the system bundle.
# ca: path/to/ca.crt
# ## The path to the public certificate. When using this option, setting the key option is required.
# cert: path/to/foo.cert
# ## The path to the private key. When using this option, setting the cert option is required.
# key: path/to/key.key
# ## If set to true, the TLS connection accepts any certificate presented by the server regardless of the hostnames it covers.
# insecureSkipVerify: true
# ## This instructs the reporter to send metrics to the OpenTelemetry Collector using gRPC.
# grpc: true
## -- enable optional CRDs for Prometheus Operator
##
## Create a dedicated metrics service for use with ServiceMonitor
# service:
# enabled: false
# labels: {}
# annotations: {}
## When set to true, it won't check if Prometheus Operator CRDs are deployed
# disableAPICheck: false
# serviceMonitor:
# metricRelabelings: []
# - sourceLabels: [__name__]
# separator: ;
# regex: ^fluentd_output_status_buffer_(oldest|newest)_.+
# replacement: $1
# action: drop
# relabelings: []
# - sourceLabels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name]
# separator: ;
# regex: ^(.*)$
# targetLabel: nodename
# replacement: $1
# action: replace
# jobLabel: traefik
# interval: 30s
# honorLabels: true
# # (Optional)
# # scrapeTimeout: 5s
# # honorTimestamps: true
# # enableHttp2: true
# # followRedirects: true
# # additionalLabels:
# # foo: bar
# # namespace: "another-namespace"
# # namespaceSelector: {}
# prometheusRule:
# additionalLabels: {}
# namespace: "another-namespace"
# rules:
# - alert: TraefikDown
# expr: up{job="traefik"} == 0
# for: 5m
# labels:
# context: traefik
# severity: warning
# annotations:
# summary: "Traefik Down"
# description: "{{ $labels.pod }} on {{ $labels.nodename }} is down"
## Tracing 分布式追踪
# -- https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/observability/tracing/overview/
tracing: {}
# openTelemetry: # traefik v3+ only
# grpc: {}
# insecure: true
# address: localhost:4317
# instana:
# localAgentHost: 127.0.0.1
# localAgentPort: 42699
# logLevel: info
# enableAutoProfile: true
# datadog:
# localAgentHostPort: 127.0.0.1:8126
# debug: false
# globalTag: ""
# prioritySampling: false
# jaeger:
# samplingServerURL: http://localhost:5778/sampling
# samplingType: const
# samplingParam: 1.0
# localAgentHostPort: 127.0.0.1:6831
# gen128Bit: false
# propagation: jaeger
# traceContextHeaderName: uber-trace-id
# disableAttemptReconnecting: true
# collector:
# endpoint: ""
# user: ""
# password: ""
# zipkin:
# httpEndpoint: http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans
# sameSpan: false
# id128Bit: true
# sampleRate: 1.0
# haystack:
# localAgentHost: 127.0.0.1
# localAgentPort: 35000
# globalTag: ""
# traceIDHeaderName: ""
# parentIDHeaderName: ""
# spanIDHeaderName: ""
# baggagePrefixHeaderName: ""
# elastic:
# serverURL: http://localhost:8200
# secretToken: ""
# serviceEnvironment: ""
# -- Global command arguments to be passed to all traefik's pods
# 启用自动检查 Traefik 的新版本
# 启用向 Traefik 官方匿名发送使用数据
#globalArguments:
# - "--global.checknewversion"
# - "--global.sendanonymoususage"
globalArguments: []
#
# Configure Traefik static configuration
# -- Additional arguments to be passed at Traefik's binary
# All available options available on https://docs.traefik.io/reference/static-configuration/cli/
## Use curly braces to pass values: `helm install --set="additionalArguments={--providers.kubernetesingress.ingressclass=traefik-internal,--log.level=DEBUG}"`
# 用于通过命令行参数向 Traefik 传递额外的配置
# 这些参数会在 Traefik 启动时应用,以便控制其行为和功能
additionalArguments: []
# - "--providers.kubernetesingress.ingressclass=traefik-internal"
# - "--log.level=DEBUG"
# -- Environment variables to be passed to Traefik's binary
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
# - name: SOME_VAR
# value: some-var-value
# - name: SOME_VAR_FROM_CONFIG_MAP
# valueFrom:
# configMapRef:
# name: configmap-name
# key: config-key
# - name: SOME_SECRET
# valueFrom:
# secretKeyRef:
# name: secret-name
# key: secret-key
# -- Environment variables to be passed to Traefik's binary from configMaps or secrets
envFrom: []
# - configMapRef:
# name: config-map-name
# - secretRef:
# name: secret-name
ports:
traefik:
port: 9000
# -- Use hostPort if set.
# hostPort: 9000
#
# -- Use hostIP if set. If not set, Kubernetes will default to 0.0.0.0, which
# means it's listening on all your interfaces and all your IPs. You may want
# to set this value if you need traefik to listen on specific interface
# only.
# hostIP: 192.168.100.10
# Override the liveness/readiness port. This is useful to integrate traefik
# with an external Load Balancer that performs healthchecks.
# Default: ports.traefik.port
# healthchecksPort: 9000
# Override the liveness/readiness scheme. Useful for getting ping to
# respond on websecure entryPoint.
# healthchecksScheme: HTTPS
# Defines whether the port is exposed if service.type is LoadBalancer or
# NodePort.
#
# -- You SHOULD NOT expose the traefik port on production deployments.
# If you want to access it from outside your cluster,
# use `kubectl port-forward` or create a secure ingress
expose: false
# -- The exposed port for this service
exposedPort: 9000
# -- The port protocol (TCP/UDP)
protocol: TCP
web:
## -- Enable this entrypoint as a default entrypoint. When a service doesn't explicitly set an entrypoint it will only use this entrypoint.
# asDefault: true
port: 8000
# hostPort: 8000
# containerPort: 8000
expose: true
exposedPort: 80
## -- Different target traefik port on the cluster, useful for IP type LB
# targetPort: 80
# The port protocol (TCP/UDP)
protocol: TCP
# -- Use nodeport if set. This is useful if you have configured Traefik in a
# LoadBalancer.
nodePort: 32080
# Port Redirections
# Added in 2.2, you can make permanent redirects via entrypoints.
# https://docs.traefik.io/routing/entrypoints/#redirection
# redirectTo: websecure
#
# Trust forwarded headers information (X-Forwarded-*).
# forwardedHeaders:
# trustedIPs: []
# insecure: false
#
# Enable the Proxy Protocol header parsing for the entry point
# proxyProtocol:
# trustedIPs: []
# insecure: false
websecure:
## -- Enable this entrypoint as a default entrypoint. When a service doesn't explicitly set an entrypoint it will only use this entrypoint.
# asDefault: true
port: 8443
# hostPort: 8443
# containerPort: 8443
# 将此端口暴露给外部
expose: true
# 暴露给外部的端口
exposedPort: 443
## -- Different target traefik port on the cluster, useful for IP type LB
# targetPort: 80
## -- The port protocol (TCP/UDP)
protocol: TCP
nodePort: 32443
## -- Specify an application protocol. This may be used as a hint for a Layer 7 load balancer.
# appProtocol: https
#
## -- Enable HTTP/3 on the entrypoint
## Enabling it will also enable http3 experimental feature
## https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/routing/entrypoints/#http3
## There are known limitations when trying to listen on same ports for
## TCP & UDP (Http3). There is a workaround in this chart using dual Service.
## https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/47249#issuecomment-587960741
http3:
enabled: false
# advertisedPort: 4443
#
## -- Trust forwarded headers information (X-Forwarded-*).
#forwardedHeaders:
# trustedIPs: []
# insecure: false
#
## -- Enable the Proxy Protocol header parsing for the entry point
#proxyProtocol:
# trustedIPs: []
# insecure: false
#
## Set TLS at the entrypoint
## https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/routing/entrypoints/#tls
tls:
enabled: true
# this is the name of a TLSOption definition
options: ""
certResolver: ""
domains: []
# - main: example.com
# sans:
# - foo.example.com
# - bar.example.com
#
# -- One can apply Middlewares on an entrypoint
# https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/middlewares/overview/
# https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/routing/entrypoints/#middlewares
# -- /!\ It introduces here a link between your static configuration and your dynamic configuration /!\
# It follows the provider naming convention: https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/providers/overview/#provider-namespace
# middlewares:
# - namespace-name1@kubernetescrd
# - namespace-name2@kubernetescrd
middlewares: []
metrics:
# -- When using hostNetwork, use another port to avoid conflict with node exporter:
# https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/wiki/Default-port-allocations
port: 9100
# hostPort: 9100
# Defines whether the port is exposed if service.type is LoadBalancer or
# NodePort.
#
# -- You may not want to expose the metrics port on production deployments.
# If you want to access it from outside your cluster,
# use `kubectl port-forward` or create a secure ingress
expose: false
# -- The exposed port for this service
exposedPort: 9100
# -- The port protocol (TCP/UDP)
protocol: TCP
# -- TLS Options are created as TLSOption CRDs
# https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/https/tls/#tls-options
# When using `labelSelector`, you'll need to set labels on tlsOption accordingly.
# Example:
# tlsOptions:
# default:
# labels: {}
# sniStrict: true
# preferServerCipherSuites: true
# customOptions:
# labels: {}
# curvePreferences:
# - CurveP521
# - CurveP384
tlsOptions: {}
# -- TLS Store are created as TLSStore CRDs. This is useful if you want to set a default certificate
# https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/https/tls/#default-certificate
# Example:
# tlsStore:
# default:
# defaultCertificate:
# secretName: tls-cert
tlsStore: {}
service:
enabled: true
## -- Single service is using `MixedProtocolLBService` feature gate.
## -- When set to false, it will create two Service, one for TCP and one for UDP.
## 控制是否使用单个 Service 来处理多协议负载均衡(TCP 和 UDP)
single: true
type: NodePort
# -- Additional annotations applied to both TCP and UDP services (e.g. for cloud provider specific config)
annotations: {}
# -- Additional annotations for TCP service only
annotationsTCP: {}
# -- Additional annotations for UDP service only
annotationsUDP: {}
# -- Additional service labels (e.g. for filtering Service by custom labels)
labels: {}
# -- Additional entries here will be added to the service spec.
# -- Cannot contain type, selector or ports entries.
spec:
ports:
externalTrafficPolicy: Local
# 客户端的原始 IP
# loadBalancerIP: "1.2.3.4"
# clusterIP: "2.3.4.5"
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
# - 192.168.0.1/32
# - 172.16.0.0/16
## -- Class of the load balancer implementation
# loadBalancerClass: service.k8s.aws/nlb
externalIPs: []
# - 1.2.3.4
## One of SingleStack, PreferDualStack, or RequireDualStack.
# ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack
## List of IP families (e.g. IPv4 and/or IPv6).
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/dual-stack/#services
# ipFamilies:
# - IPv4
# - IPv6
##
## -- An additionnal and optional internal Service.
## Same parameters as external Service
# internal:
# type: ClusterIP
# # labels: {}
# # annotations: {}
# # spec: {}
# # loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
# # externalIPs: []
# # ipFamilies: [ "IPv4","IPv6" ]
autoscaling:
# -- Create HorizontalPodAutoscaler object.
enabled: false
# minReplicas: 1
# maxReplicas: 10
# metrics:
# - type: Resource
# resource:
# name: cpu
# target:
# type: Utilization
# averageUtilization: 60
# - type: Resource
# resource:
# name: memory
# target:
# type: Utilization
# averageUtilization: 60
# behavior:
# scaleDown:
# stabilizationWindowSeconds: 300
# policies:
# - type: Pods
# value: 1
# periodSeconds: 60
persistence:
# 持久化存储
# -- Enable persistence using Persistent Volume Claims
# ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/persistent-volumes/
# It can be used to store TLS certificates, see `storage` in certResolvers
enabled: false
name: data
# existingClaim: ""
accessMode: ReadWriteOnce
size: 128Mi
# storageClass: ""
# volumeName: ""
path: /data
annotations: {}
# -- Only mount a subpath of the Volume into the pod
# subPath: ""
# -- Certificates resolvers configuration
certResolvers: {}
# letsencrypt:
# # for challenge options cf. https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/https/acme/
# email: email@example.com
# dnsChallenge:
# # also add the provider's required configuration under env
# # or expand then from secrets/configmaps with envfrom
# # cf. https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/https/acme/#providers
# provider: digitalocean
# # add futher options for the dns challenge as needed
# # cf. https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/https/acme/#dnschallenge
# delayBeforeCheck: 30
# resolvers:
# - 1.1.1.1
# - 8.8.8.8
# tlsChallenge: true
# httpChallenge:
# entryPoint: "web"
# # It has to match the path with a persistent volume
# storage: /data/acme.json
# -- If hostNetwork is true, runs traefik in the host network namespace
# To prevent unschedulabel pods due to port collisions, if hostNetwork=true
# and replicas>1, a pod anti-affinity is recommended and will be set if the
# affinity is left as default.
# 将直接绑定到节点的主机网络接口
hostNetwork: false
# -- Whether Role Based Access Control objects like roles and rolebindings should be created
rbac:
enabled: true
# If set to false, installs ClusterRole and ClusterRoleBinding so Traefik can be used across namespaces.
# If set to true, installs Role and RoleBinding. Providers will only watch target namespace.
namespaced: false
# Enable user-facing roles
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/rbac/#user-facing-roles
# aggregateTo: [ "admin" ]
# -- Enable to create a PodSecurityPolicy and assign it to the Service Account via RoleBinding or ClusterRoleBinding
podSecurityPolicy:
enabled: false
# -- The service account the pods will use to interact with the Kubernetes API
serviceAccount:
# If set, an existing service account is used
# If not set, a service account is created automatically using the fullname template
name: ""
# -- Additional serviceAccount annotations (e.g. for oidc authentication)
serviceAccountAnnotations: {}
# -- The resources parameter defines CPU and memory requirements and limits for Traefik's containers.
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "512Mi"
limits:
cpu: "500m"
memory: "1024Mi"
# -- This example pod anti-affinity forces the scheduler to put traefik pods
# -- on nodes where no other traefik pods are scheduled.
# It should be used when hostNetwork: true to prevent port conflicts
affinity: {}
# podAntiAffinity:
# requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
# - labelSelector:
# matchLabels:
# app.kubernetes.io/name: '{{ template "traefik.name" . }}'
# app.kubernetes.io/instance: '{{ .Release.Name }}-{{ .Release.Namespace }}'
# topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
# -- nodeSelector is the simplest recommended form of node selection constraint.
nodeSelector: {}
# -- Tolerations allow the scheduler to schedule pods with matching taints.
tolerations: []
# -- You can use topology spread constraints to control
# how Pods are spread across your cluster among failure-domains.
topologySpreadConstraints: []
# This example topologySpreadConstraints forces the scheduler to put traefik pods
# on nodes where no other traefik pods are scheduled.
# - labelSelector:
# matchLabels:
# app: '{{ template "traefik.name" . }}'
# maxSkew: 1
# topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
# whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule
# -- Pods can have priority.
# -- Priority indicates the importance of a Pod relative to other Pods.
priorityClassName: ""
# -- Set the container security context
# -- To run the container with ports below 1024 this will need to be adjusted to run as root
securityContext:
capabilities:
drop: [ALL]
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
podSecurityContext:
# /!\ When setting fsGroup, Kubernetes will recursively change ownership and
# permissions for the contents of each volume to match the fsGroup. This can
# be an issue when storing sensitive content like TLS Certificates /!\
# fsGroup: 65532
# -- Specifies the policy for changing ownership and permissions of volume contents to match the fsGroup.
fsGroupChangePolicy: "OnRootMismatch"
# -- The ID of the group for all containers in the pod to run as.
runAsGroup: 65532
# -- Specifies whether the containers should run as a non-root user.
runAsNonRoot: true
# -- The ID of the user for all containers in the pod to run as.
runAsUser: 65532
#
# -- Extra objects to deploy (value evaluated as a template)
#
# In some cases, it can avoid the need for additional, extended or adhoc deployments.
# See #595 for more details and traefik/tests/values/extra.yaml for example.
extraObjects: []
# This will override the default Release Namespace for Helm.
# It will not affect optional CRDs such as `ServiceMonitor` and `PrometheusRules`
# namespaceOverride: traefik
#
## -- This will override the default app.kubernetes.io/instance label for all Objects.
# instanceLabelOverride: traefik$ helm upgrade --install traefik ./ -f ./xin-traefik-valuse.yaml --namespace kube-system
Release "traefik" has been upgraded. Happy Helming!
NAME: traefik
LAST DEPLOYED: Wed Aug 28 11:18:25 2024
NAMESPACE: kube-system
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 3
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
Traefik Proxy v2.10.4 has been deployed successfully on kube-system namespace !
$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system -l app.kubernetes.io/name=traefik
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
traefik-6d59d5fc9-vk9gk 1/1 Running 0 17h安装完成后我们可以通过查看 Pod 的资源清单来了解 Traefik 的运行方式:
$ kubectl get deploy -n kube-system traefik -o yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
......
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --entrypoints.metrics.address=:9100/tcp
- --entrypoints.traefik.address=:9000/tcp
- --entrypoints.web.address=:8000/tcp
- --entrypoints.websecure.address=:8443/tcp
- --api.dashboard=true
- --ping=true
- --metrics.prometheus=true
- --metrics.prometheus.entrypoint=metrics
- --providers.kubernetescrd
- --providers.kubernetescrd.allowCrossNamespace=true
- --providers.kubernetescrd.allowExternalNameServices=true
- --providers.kubernetescrd.allowEmptyServices=true
- --providers.kubernetesingress
- --providers.kubernetesingress.allowExternalNameServices=true
- --providers.kubernetesingress.allowEmptyServices=true
- --entrypoints.websecure.http.tls=true
image: registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/xxk8s/traefik:v2.10.4
......其中 entryPoints 属性定义了 web 和 websecure 这两个入口点的,并开启 kubernetesingress 和 kubernetescrd 这两个 provider,也就是我们可以使用 Kubernetes 原本的 Ingress 资源对象,也可以使用 Traefik 自己扩展的 IngressRoute 这样的 CRD 资源对象。
创建Dashboard-IngressRoute
我们可以首先创建一个用于 Dashboard 访问的 IngressRoute 资源清单:
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: IngressRoute
metadata:
name: traefik-dashboard
namespace: kube-system
spec:
entryPoints:
- web
routes:
- match: Host(`traefik.xinn.com`)
kind: Rule
services:
- name: api@internal
kind: TraefikService
$ kubectl get ingressroute -n kube-system
NAME AGE
traefik-dashboard 19m其中的 TraefikService 是 Traefik Service 的一个 CRD 实现,这里我们使用的 api@internal 这个 TraefikService,表示我们访问的是 Traefik 内置的应用服务。
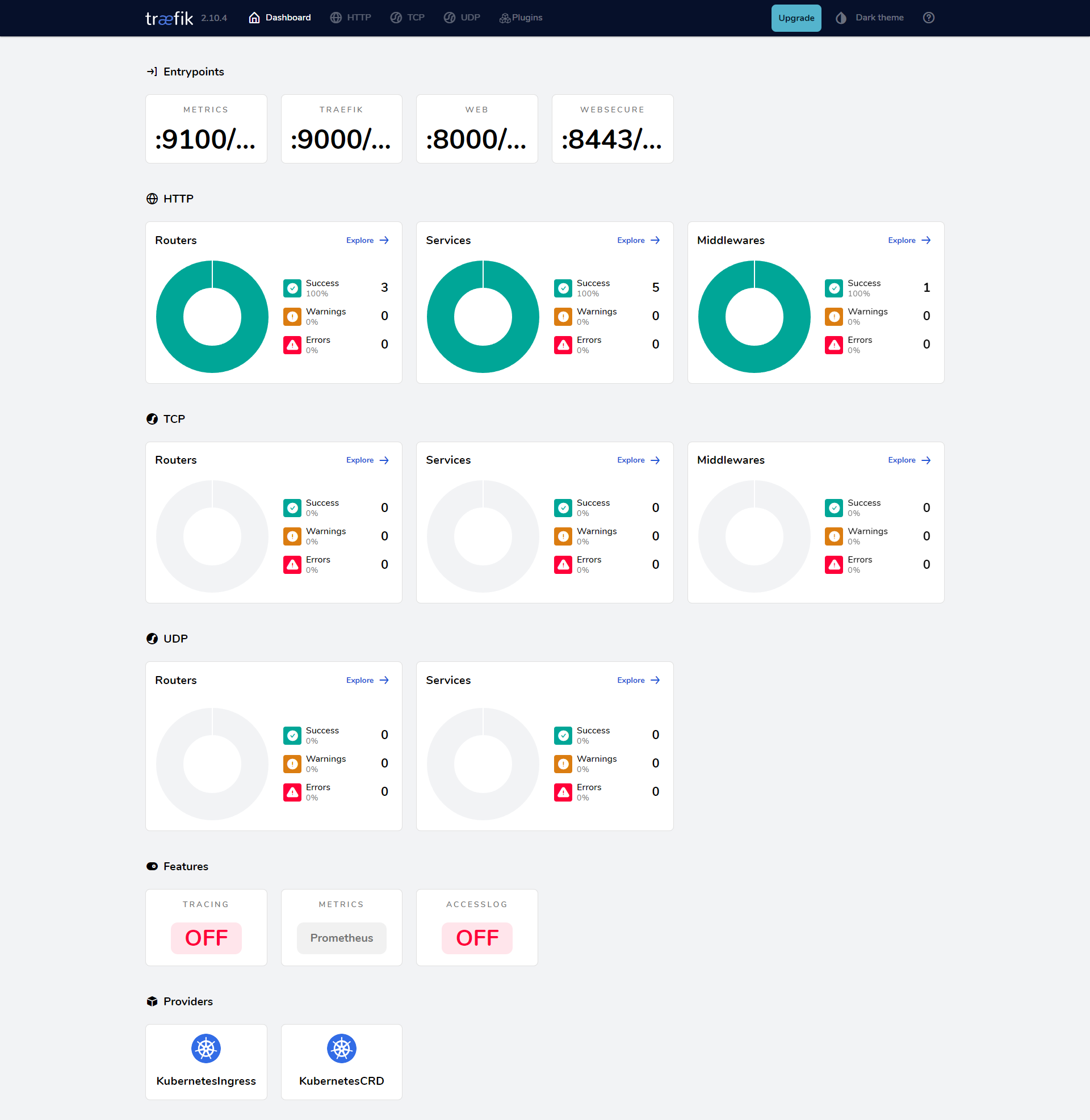
部署完成后我们可以通过在本地 /etc/hosts 中添加上域名 traefik.xinn.com 的映射即可访问 Traefik 的 Dashboard 页面了:
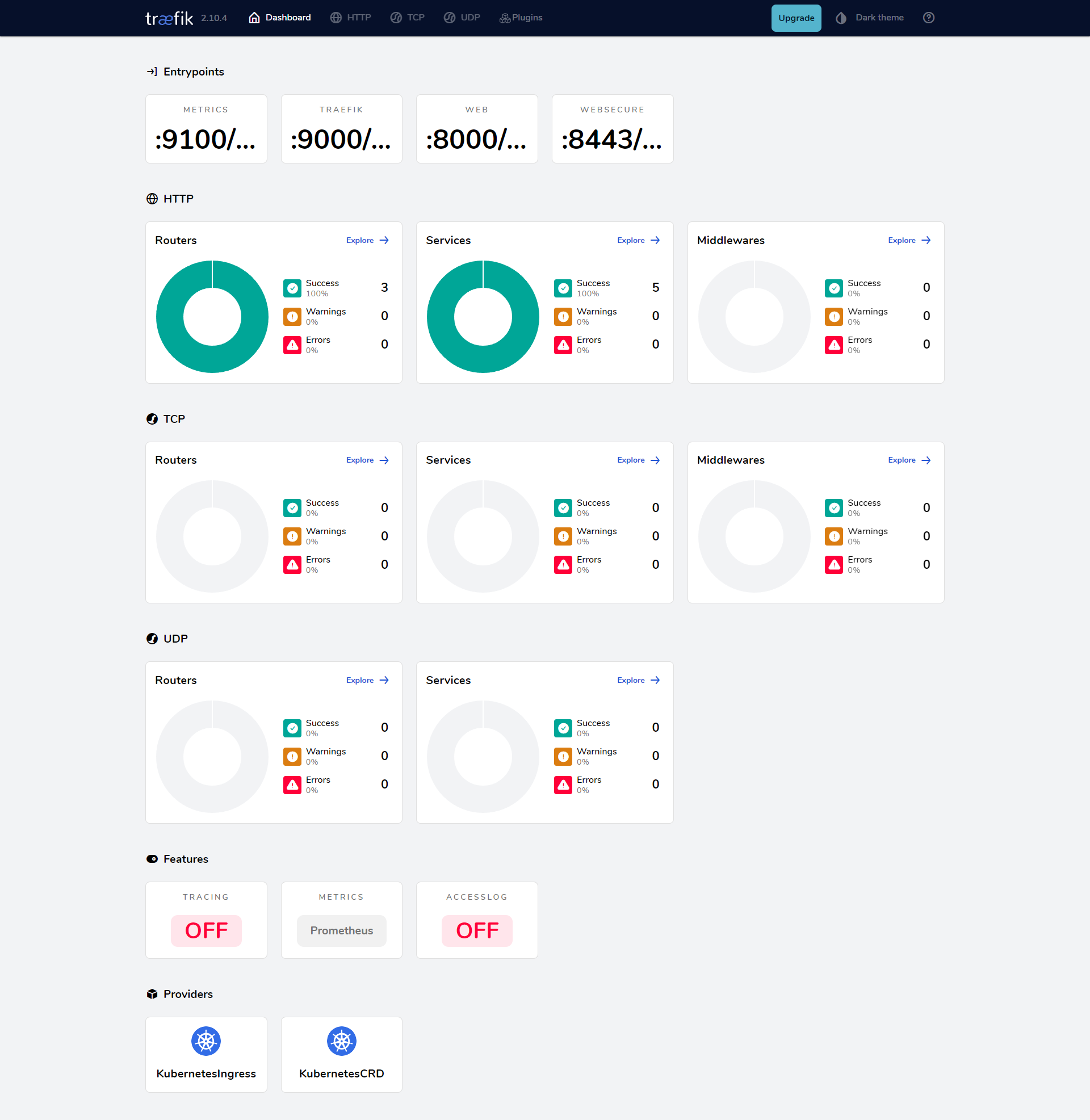
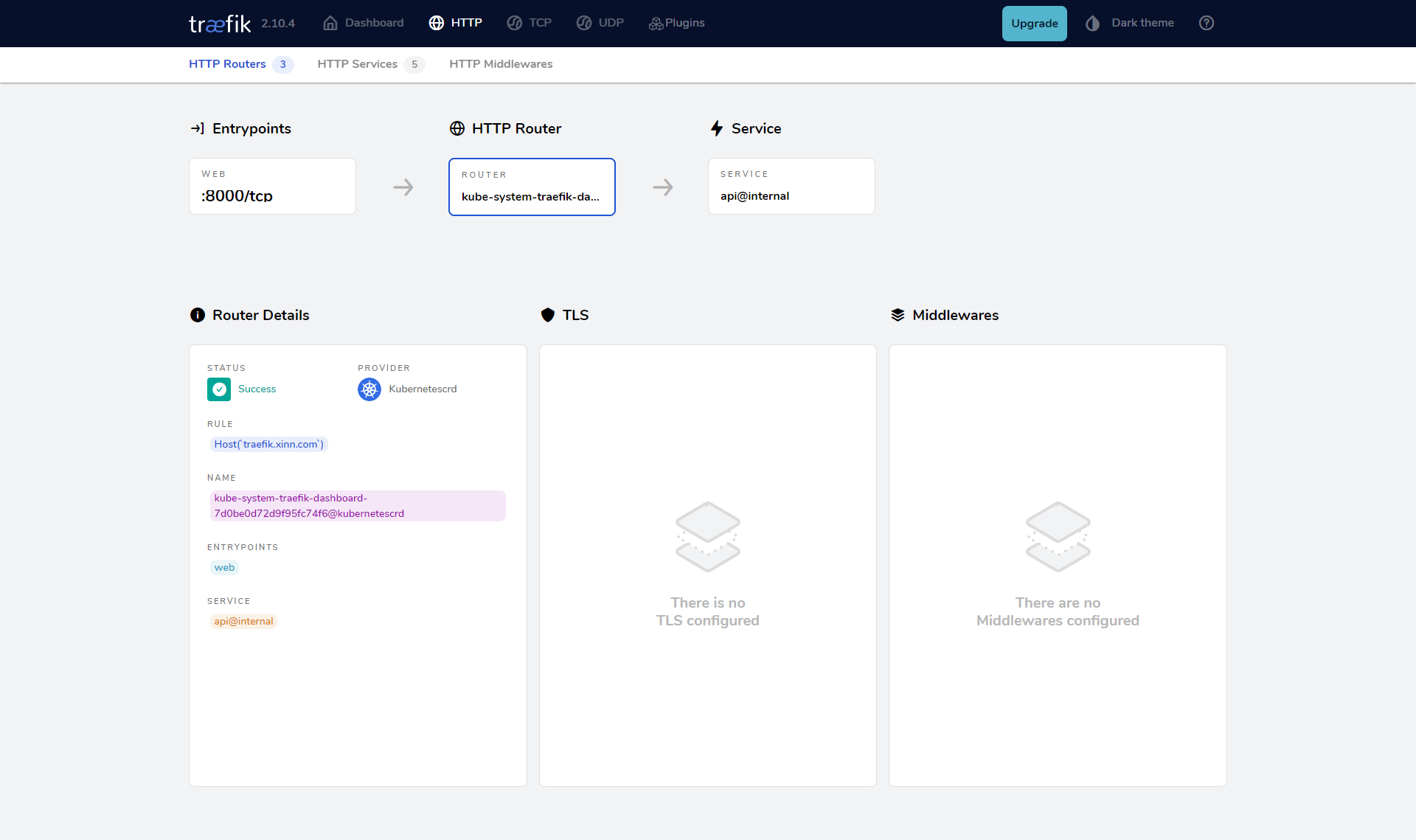
注意
另外需要注意的是默认情况下 Traefik 的 IngressRoute 已经允许跨 namespace 进行通信了,可以通过设置参数 --providers.kubernetescrd.allowCrossNamespace=true 开启(默认已经开启),开启后 IngressRoute 就可以引用 IngressRoute 命名空间以外的其他命名空间中的任何资源了。
如果要让 Traefik 去处理默认的 Ingress 资源对象,则我们就需要使用名为 traefik的 IngressClass 了,因为没有指定默认的:
$ kubectl get ingressclass
NAME CONTROLLER PARAMETERS AGE
nginx k8s.io/ingress-nginx <none> 46h
traefik-class traefik.io/ingress-controller <none> 17h
#traefik-class名称是在上面的value文件中定义的创建如下所示的一个 Ingress 资源对象,这里的核心是 ingressClassName 要指向 traefik 这个 IngressClass:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: my-nginx-by-traefik
namespace: default
spec:
ingressClassName: traefik-class # 使用 traefk 的 IngressClass
rules:
- host: ngdemo-by-traefik.xinn.com # 将域名映射到 my-nginx 服务
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service: # 将所有请求发送到 my-nginx 服务的 80 端口
name: my-nginx
port:
number: 80直接创建上面的资源对象即可:
$ kubectl get ingress
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
my-nginx nginx ngdemo.qikqiak.com 192.168.31.31 80 3d23h
my-nginx-by-traefik traefik ngdemo-by-traefik.qikqiak.com 80 4s然后就可以正常访问 ngdemo-by-traefik.xinn.com 域名了:
$ curl ngdemo-by-traefik.xinn.com
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>添加 Traefik Dashboard 的基本身份验证
为了给 Traefik Dashboard 添加密码保护,您可以使用 Traefik 的中间件(Middleware) 功能,通过 IngressRoute 结合 BasicAuth 中间件实现基本身份验证。
1. 创建 BasicAuth Secret
首先,您需要为基本身份验证创建一个包含用户名和密码的 Kubernetes Secret。可以使用 htpasswd 工具生成密码文件:
# 安装 htpasswd 工具
sudo apt-get install apache2-utils
# 生成带有用户名和密码的 htpasswd 文件
root@master01:/k8s-traefik# htpasswd -nb xin "N47j#u4[£dss" > auth这个命令会输出类似于:
admin:$apr1$eI8D7f3v$u1JiMd7J4j4OUb9BrK13K1然后将此加密后的密码保存到 Kubernetes Secret 中:
root@master01:/k8s-traefik# kubectl create secret generic traefik-dashboard-auth --from-file=users=auth -n kube-system
secret/traefik-dashboard-auth created这个命令会在 kube-system 命名空间中创建一个名为 traefik-dashboard-auth 的 Secret。
2. 定义 BasicAuth 中间件
接下来,您需要创建一个 Traefik 中间件来使用 BasicAuth 进行身份验证。以下是 BasicAuth 中间件的示例:
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: Middleware
metadata:
name: traefik-dashboard-auth
namespace: kube-system
spec:
basicAuth:
secret: traefik-dashboard-auth
realm: TraefikDashboard这个中间件会引用之前创建的 Secret,并为 Dashboard 添加基本身份验证。
3. 更新 IngressRoute 以使用 BasicAuth 中间件
接下来,您需要在 IngressRoute 中引用这个身份验证中间件:
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: IngressRoute
metadata:
name: traefik-dashboard
namespace: kube-system
spec:
entryPoints:
- web
routes:
- match: Host(`traefik.example.com`) && (PathPrefix(`/dashboard`) || PathPrefix(`/api`))
kind: Rule
services:
- name: api@internal
kind: TraefikService
middlewares:
- name: traefik-dashboard-auth # 添加中间件进行身份验证在这个配置中:
middlewares部分引用了我们定义的traefik-dashboard-auth中间件,从而在访问 Traefik Dashboard 时启用了基本身份验证。
4. 应用这些资源
现在,您可以将这些资源应用到 Kubernetes 集群中:
kubectl apply -f traefik-dashboard-auth.yaml
kubectl apply -f traefik-dashboard-ingressroute.yaml5. 访问带有密码保护的 Dashboard
之后,当您访问 Traefik Dashboard 时,会提示您输入用户名和密码:
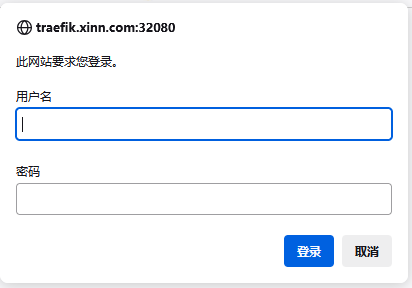
成功登录